At North Mead Primary Academy, we provide a high quality geography education, which aims to inspire children’s curiosity about the world and its people. Our creative curriculum teaches children an understanding of places and environments. Through their work in geography, children gain a deepened understanding about the make-up of their local area and compare it to other regions in the United Kingdom and the rest of the world. Children are taught to learn how to draw, interpret and follow maps and develop their skill of research, investigation, analysis and problem solving. Geography teaching inspires our children to investigate the physical world, which in turn enables them to think about the importance of issues such as sustainable development and how it affects humanity.
Teaching and learning in geography is often based through enquiry-based activities to promote independent learning. Children are given increased opportunities to formulate appropriate geographical questions, develop research skills and evaluate a range of materials to inform opinions. These skills provide children to strengthen their understanding and skill of geographical enquiry. Children are encouraged to use geographical vocabulary to support their reasoning skills. Wherever possible, children are involved in “real” geography. Teachers use the school environment and the local area to support teaching and learning of mapping skills, physical geography and human geography.
Geography is taught through our book based immersive curriculum with two topics each year having a Geography focus. These are shown in the Geography knowledge organisers.
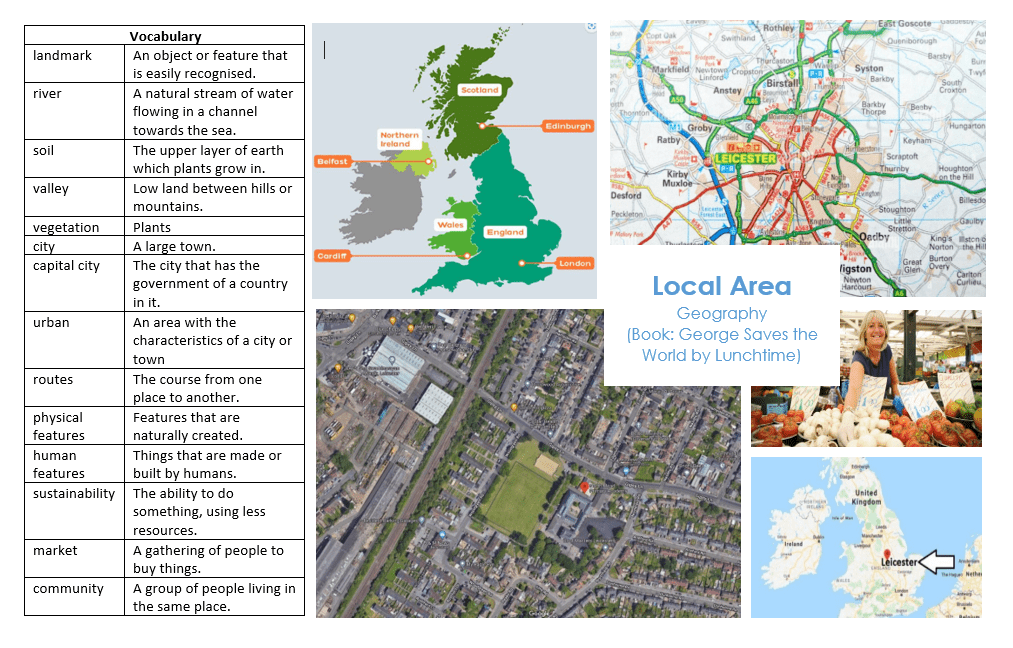
Year 1 George Saves the world by Lunchtime
Geographical skills and fieldwork
- Use simple compass directions (N,S, E and W) and locational language to describe the location of features on a route.
- Use atlases to identify the UK and its countries.
- Use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the geography of their school and its grounds and the key human and physical features of its surrounding environment
- Use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognize landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a key – Sketch a map of the school
Geographical Questions:
- What human features can you identify on a map?
- What physical features can you identify on a map?
- Can you identify the four countries of the UK and their capital cities?
- What human and physical features of Leicester can you describe?
- Can you identify Leicester on a map?
- Can you follow routes across a map?
- Can you explain why it is good to buy fruit and vegetables from the market?
- Can you explain why it can be more sustainable to grow your own vegetables
As a geographer
- Use an atlas to locate countries in the UK and their capital cities
- Use compass directions to describe a route
- Identify human and physical features around North Mead
- Use aerial maps and plan perspectives
- Create a simple map
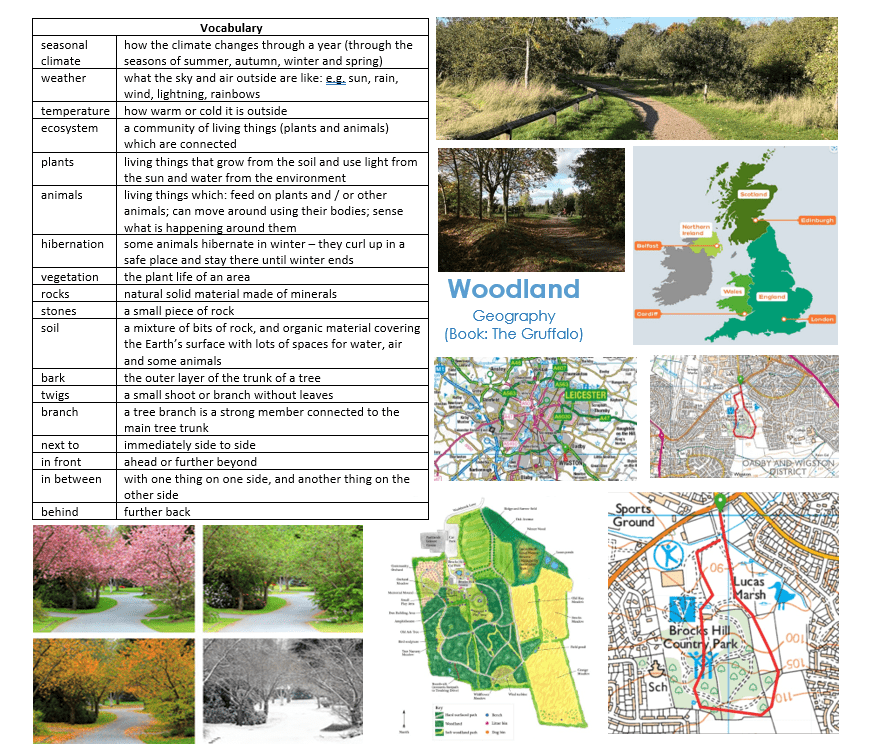
Recap from The Gruffalo
- Brocks Hill is in a forest
- Maps to describe features of Brocks Hill
- Seasonal Weather
Year 1 The Gruffalo
As a geographer
- Identify human and physical features around Brocks Hill Country Park
- Use maps and aerial maps to recognise landmarks and physical features
- Create a simple map
- Use binoculars to find wildlife and map features
- Use beakers to collect soil samples and insects
Recap from Reception
- Explore the natural world, making observations and drawing pictures of animals and plants.
- Know similarities and differences between the natural world and contrasting environments, drawing on their experiences and class reading.
- Understand important processes and changes in the natural world including the seasons and changing states of matter.
Geographical skills and fieldwork:
- Use atlases to identify the UK and its countries.
- Use simple locational and directional language [e.g. near and far; left and right] and compass directions (N,S, E and W) to describe the location of features on a map
- Identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the UK
- Use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a key – Sketch a map of the school
Geographical Questions
- How would a woodland (like Brocks Hill Country Park) look different in the different seasons?
- Can you draw a map of Brock Hill based on maps you have looked at and having been there?
- What are the physical features of Brocks Hill Country Park?
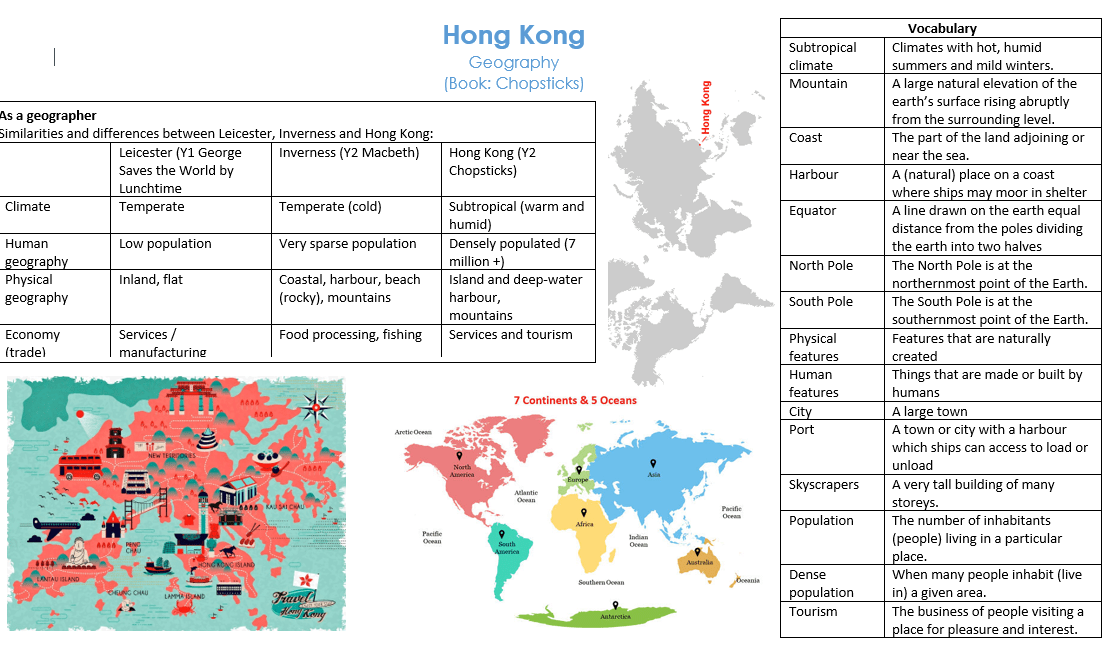
Year 2 Chopsticks
Recap from Year 1
- Leicester is a city in England
- England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland make up the UK
- Directional language (near, far, left, right, north, south, east, west)
Geographical skills and fieldwork
- Use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features.
- Use simple compass directions (N,S, E and W) and locational language to describe the location of features on a map.
Geographical Questions:
- Can you identify physical characteristics of Hong Kong?
- Can you identify human features of Hong Kong?
- Can you give reasons for geographical similarities and differences between Inverness, Leicester and Hong Kong?
- Can you explain why Hong Kong is such a large city when compared with Leicester or Inverness?
- Can you describe the climate of Hong Kong and relate this to the Equator, North and South poles
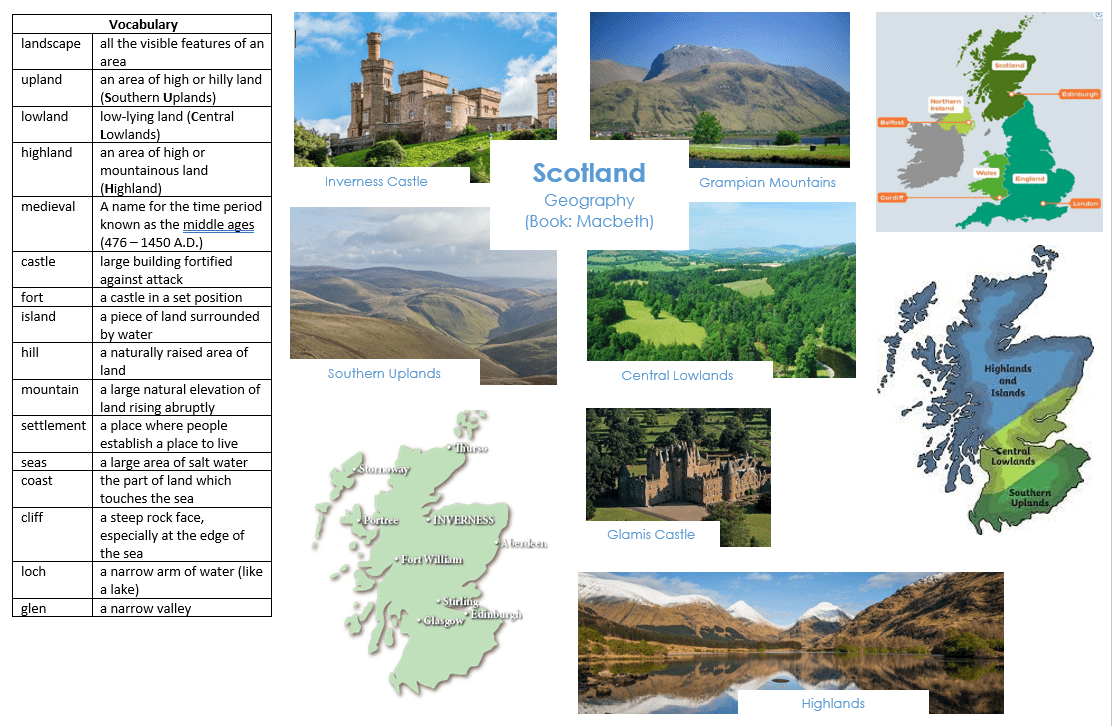
Year 2 Macbeth
Year 1
- The United Kingdom (UK) has four countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
- Leicester is in England. North Mead is in Leicester.
- Leicester has a moderate climate
Geographical skills and fieldwork
- Use worlds maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries
- Use simple compass directions (N,S, E and W) and locational language to describe the location of features on a route.
- Use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features
Geographical Questions:
- What human features can you identify on a map?
- What physical features can you identify on a map?
- Can you identify the four countries of the UK and their capital cities?
- What human and physical features of Scotland can you identify?
- Can you identify Inverness on a map?
- Can you follow routes across a map?
- Can you identify the characteristics of the four countries of the United Kingdom?
As a geographer
- Identify characteristics of the four countries which make up the United Kingdom.
- Use aerial photographs and maps to identify the human and physical geography of Scotland.
Year 2 Macbeth
Year 1
- The United Kingdom (UK) has four countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
- Leicester is in England. North Mead is in Leicester.
- Leicester has a moderate climate
Geographical skills and fieldwork
- Use worlds maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries
- Use simple compass directions (N,S, E and W) and locational language to describe the location of features on a route.
- Use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features
Geographical Questions:
- What human features can you identify on a map?
- What physical features can you identify on a map?
- Can you identify the four countries of the UK and their capital cities?
- What human and physical features of Scotland can you identify?
- Can you identify Inverness on a map?
- Can you follow routes across a map?
- Can you identify the characteristics of the four countries of the United Kingdom?
As a geographer
- Identify characteristics of the four countries which make up the United Kingdom.
- Use aerial photographs and maps to identify the human and physical geography of Scotland.

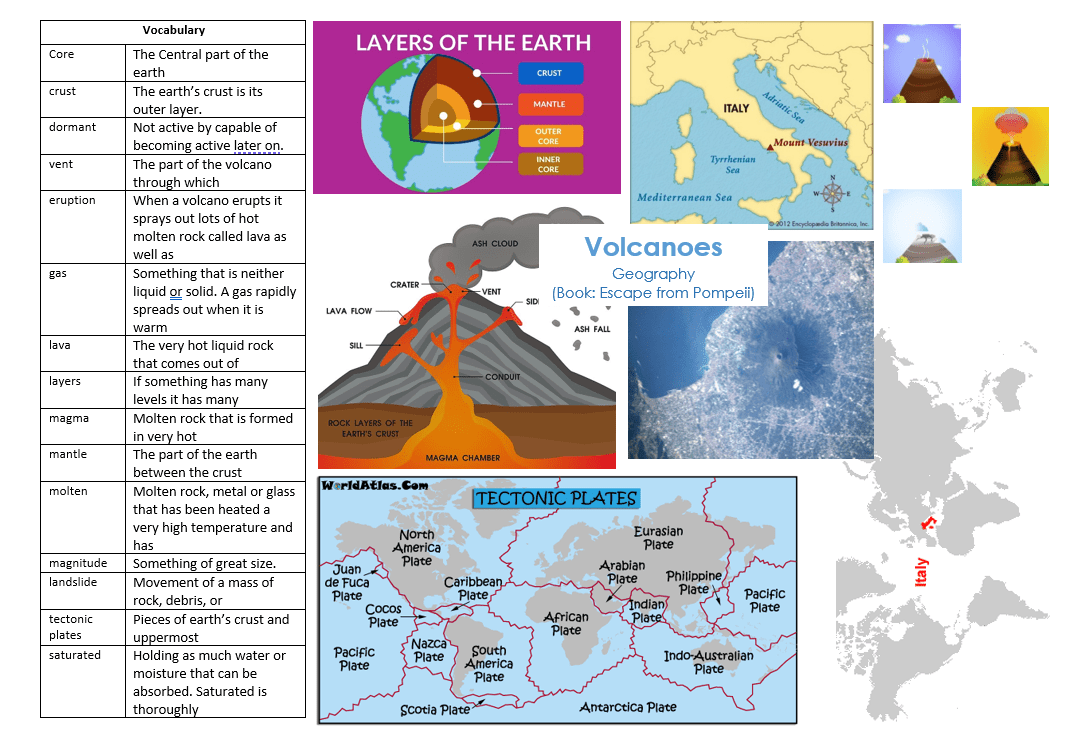
Year 3 Escape from Pompeii
KS1 (England [Leicester], Scotland [Inverness], China [Hong Kong])
Revise on world map:
- 7 Continents + 5 oceans
- UK: 4 countries and their capital cities
- Physical and human features
- Compass directions (N,S,E,W)
Geographical skills and fieldwork:
- Locate Italy on a world map and European map
- Study topographical maps – establish Mount Vesuvius is a dominant topographical, physical feature
- Slopes of Vesuvius have rich, fertile soil and the plains are easy to farm (grow grapes). The river Sarno provides water
- Identify the position of Italy: latitude, longitude (Northern Hemisphere), and in relation to the Tropic of Cancer.
Geographical Questions
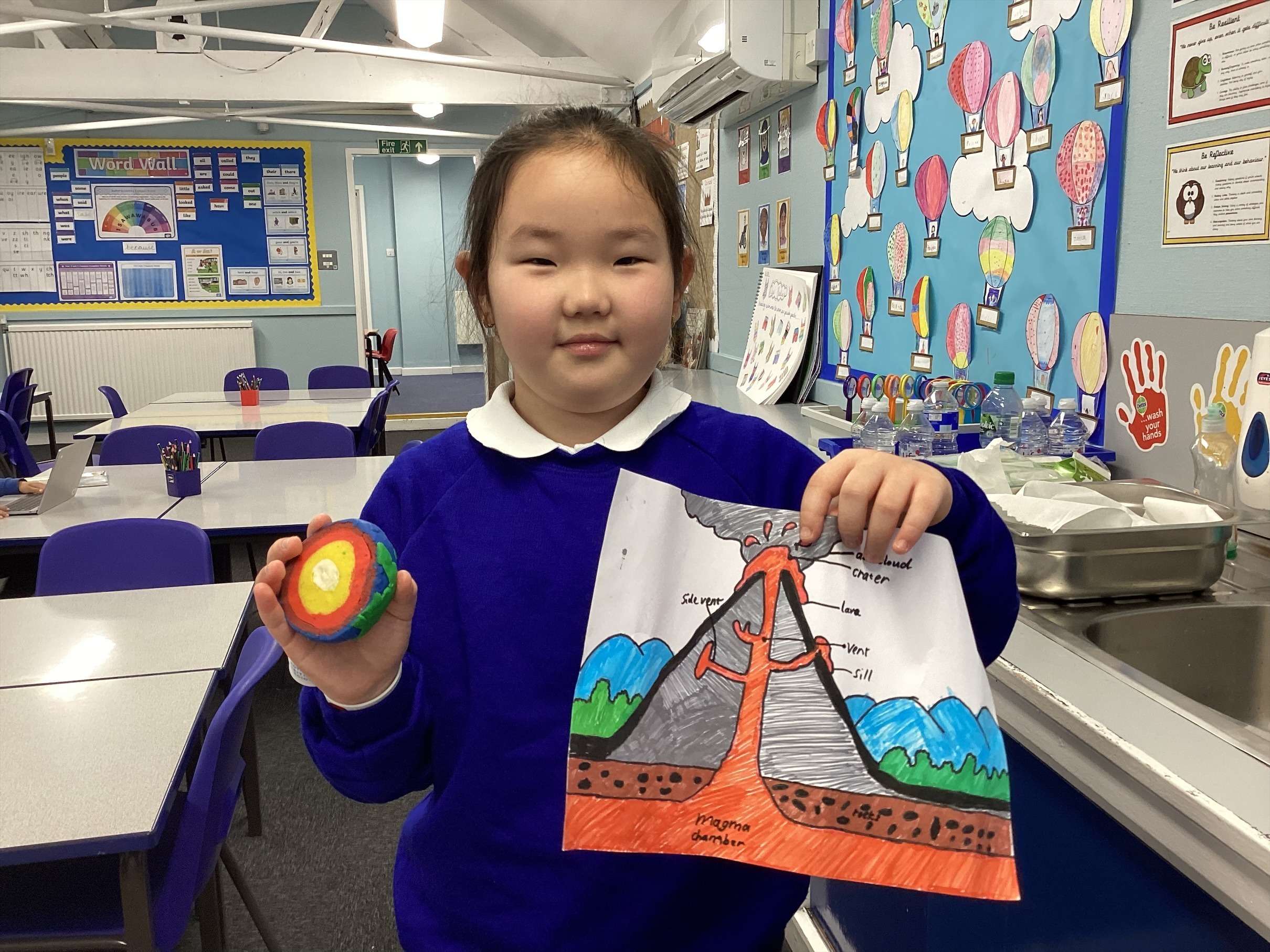
- Can you explain what happens when a volcano erupts?
- Can you name and explain the layers of the earth?
- Can you explain the benefits and drawbacks of volcanic eruptions?
- What is the climate like in Pompeii? (How does this compare to Leicester, Inverness, Hong Kong?)
As a geographer
- Beacon hill is a dormant volcano. Imagine it erupted. What would the consequences be?
- Use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs and digital technologies.
Year 3 Iron Man
As a geographer
-
- Complete a ‘tide in a drawer’ experiment: use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present physical features
- Use maps and atlases to locate countries and describe features studied
KS1 (England [Leicester], Scotland [Inverness], China [Hong Kong])
Revise on world map:
- 7 Continents + 5 oceans
- UK: 4 countries and their capital cities
- Physical and human features
- Compass directions (N, S, E, W)
Geographical skills and fieldwork:
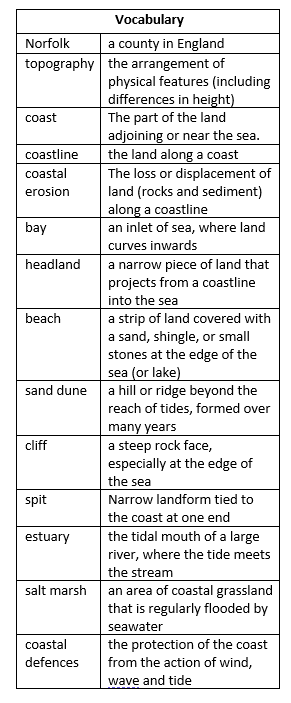
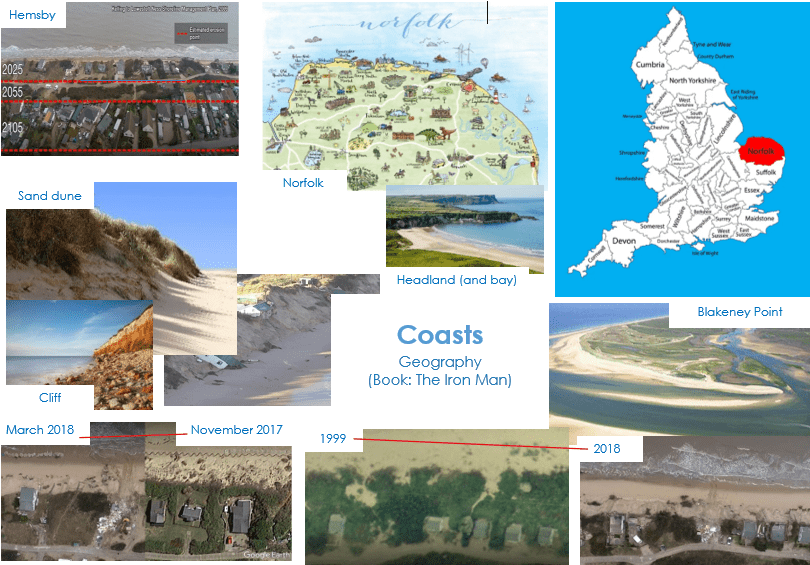
- Locate the geographical region Norfolk on a map of the UK and identify its topographical features
- Identify Norfolk’s 90 mile long coastline
- Identify Hemsby on a map of Norfolk
- Understand the interaction between human and physical processes, and the formation and use of landscapes
- Understand coastal erosion processes: hydraulic action, abrasion and corrasion
- Identify coastal features: bay, headland, beach, coastal defences, sand dunes, cliffs, estuaries, spit
- Identify the position of Norfolk: latitude, longitude (Northern Hemisphere), and in relation to the Tropic of Cancer
Geographical Questions
- Can you explain how the coastal erosion if affecting people in Hemsby?
- How have people in Hemsby interacted with their environment?
- Can you identify the features of a coastline?
Can you explain why Norfolk does not have any headlands?
Year 4 the Butterfly
As a geographer
- Visit West Midlands Safari Park
- Investigate how animals whose habitat is normally the savannah (veld) are living in the UK (temperate climate) – What adaptions are humans having to make to allow these animals to live in the UKJ?
KS1 (England [Leicester], Scotland [Inverness], China [Hong Kong])
Revise on world map:
- 7 Continents + 5 oceans
- UK: 4 countries and their capital cities
- Physical and human features
- Compass directions (N, S, E, W)
Geographical skills and fieldwork:
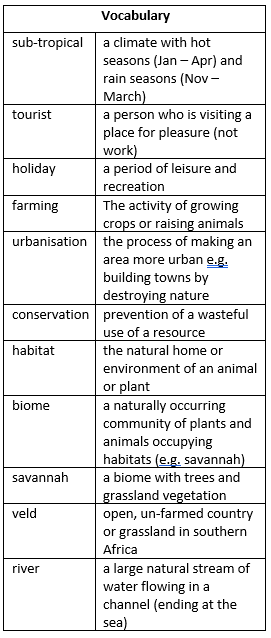
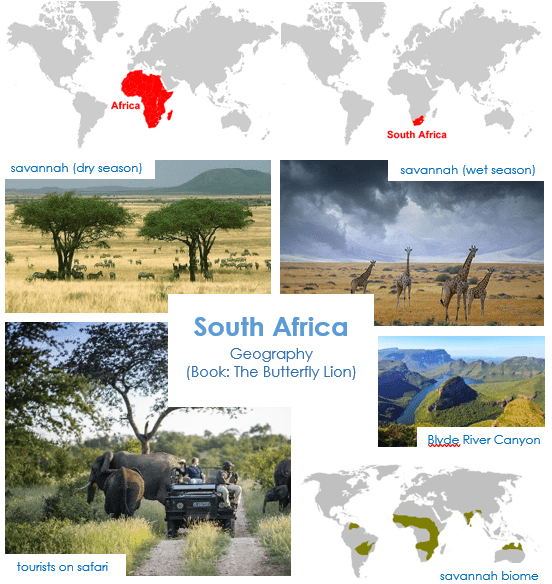
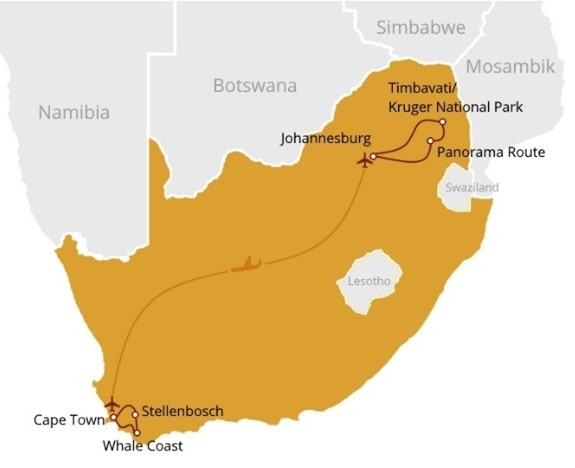
- Locate the continent Africa on a world map / Locate the country South Africa on a world map.
- Locate the Timbavati National Park within South Africa
- Identify the countries and oceans surrounding South Africa
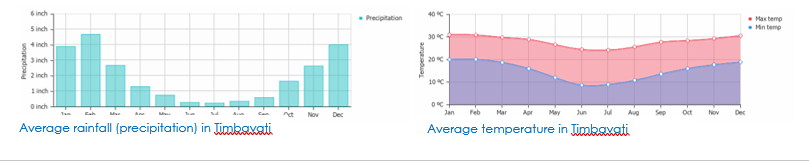
- The Eastern side of South Africa had a sub-tropical climate
- Timbavati is a popular tourist destination.
- Understand the interaction between human processes (farming and urbanisation) and the environment; the Timbavati National Park was established by conservationists to protect wildlife and habitats from farming.
- Identify the position of South Africa: latitude, longitude (Southern Hemisphere), and in relation to the Tropic of Capricorn
Geographical Questions
- Can you list the features of a savannah biome?
- Can you explain how humans interact with this biome in the Timbavati national park?
- How does a savannah biome compare with other climate’s that you have studied?
Year 4 The Kapok Tree
As a geographer
- Complete
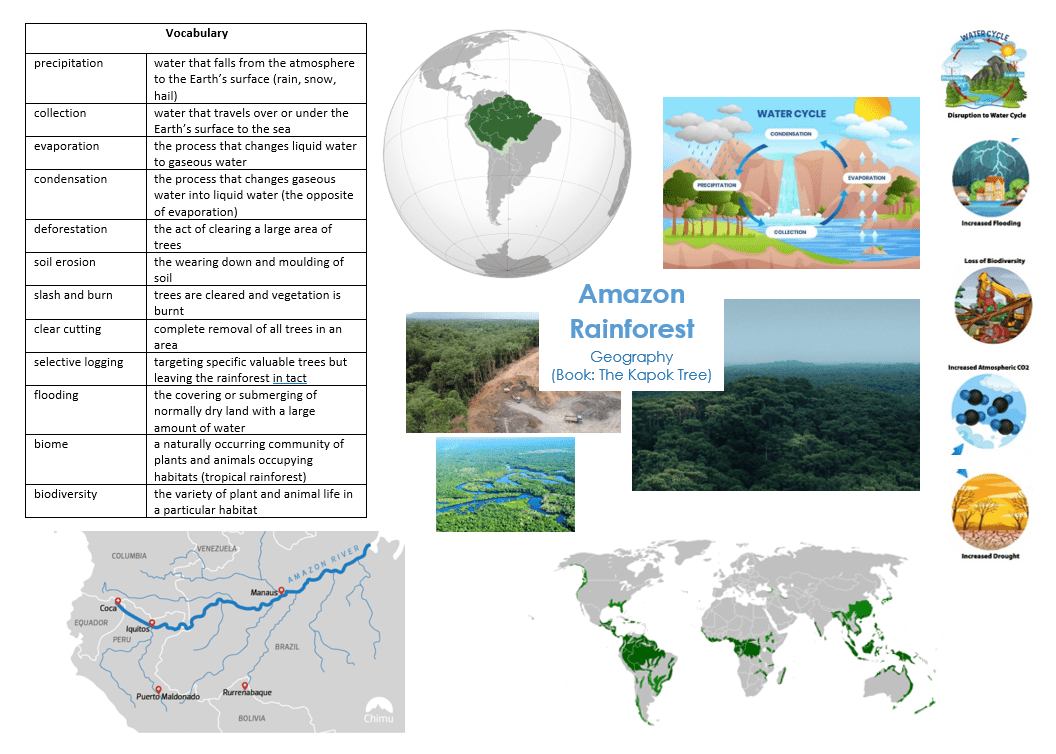
The Amazon rainforest:
- is the largest tropical rainforest in the world
- accounts for more than half of the entire world’s remaining rainforests
- is home to 10% of the known species in this world
- is also referred to as the ‘Lungs of the Planet’ because it produces more than 20% of the world’s oxygen.
- is home to around 250,000 native people.
- has many dangerous species of snakes, spiders.
- Understand the distribution of natural resources (e.g. Amazon Rainforest – mining and logging) and how this affects the economic activity
The Amazon River:
- flows through Amazon Rainforest
- has its source in the Andes mountain range and its mouth flows into the Atlantic Ocean
- is approximately 4000 miles long
KS1 (England [Leicester], Scotland [Inverness], China [Hong Kong])
Revise on world map:
- 7 Continents + 5 oceans
- UK: 4 countries and their capital cities
- Physical and human features
- Compass directions (N, S, E, W)
Geographical skills and fieldwork:
- Locate the continent South America on a world map / Locate the countries Brazil, Boliva, Peru, Ecuador, Columbia and Venezuela in South America on a World map
- Understand the interaction between human processes (deforestation and farming) and the environment; the water cycle, the cardon cycle
- Identify the position of South America: latitude, longitude (Southern Hemisphere), and in relation to the Equator and Tropics.
Geographical Questions
- Can you explain the water cycle?
- Can you explain the effects of deforestation?
- Can you name the main countries the Amazon Rainforest is located in?
- Can you compare the rainfall in the UK, with the rainfall in the Amazon Rainforest?
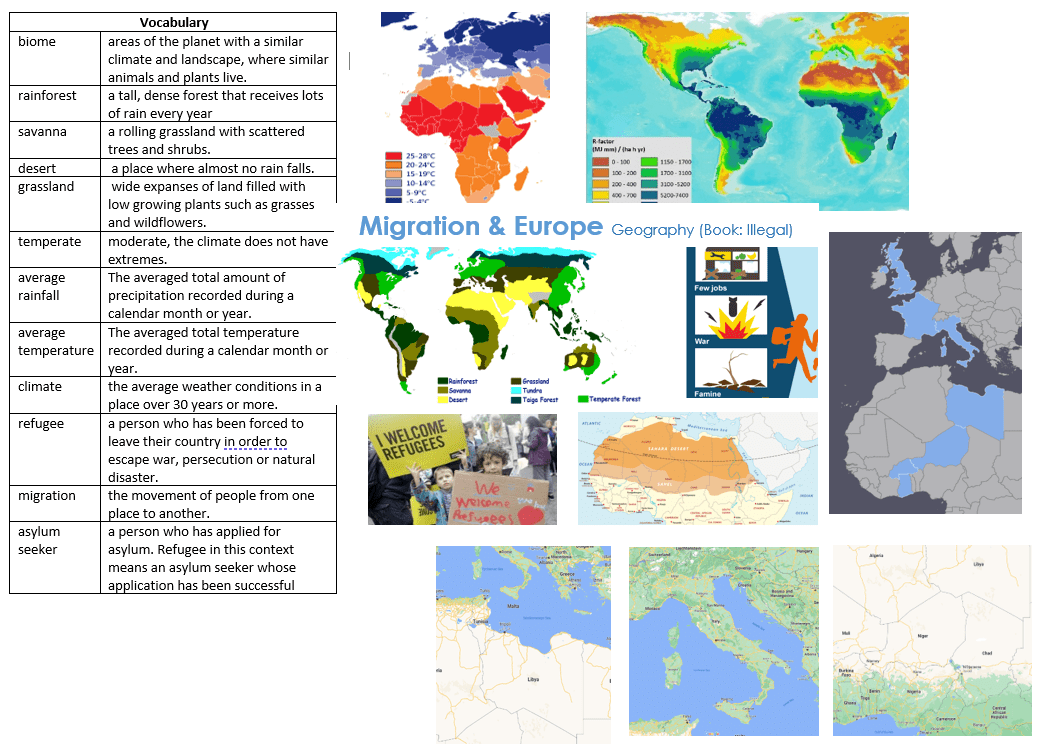
Year 5 Illegal
As a geographer
- Use maps, atlases and digital mapping to locate countries and describe features studied
- Interpret a range of sources of geographical information including diagrams and aerial photos
KS1 (England [Leicester], Scotland [Inverness], China [Hong Kong])
Revise on world map:
- 7 Continents + 5 oceans
- UK: 4 countries and their capital cities
- Physical and human features
- Compass directions (N, S, E, W)
Geographical skills and fieldwork:
- Understand migration (having to leave a country) and asylum seekers
- Locate the continent Europe and Africa on a world map
- Locate the countries Niger, Libya, Italy, France and England on a World map
- Locate the Mediterranean Sea and the Sahara Desert on a world map
- Understand the interaction between human processes (migration) and the environment: deserts and seas
- Identify the position of the Sahara Desert: latitude, longitude (Northern Hemisphere), and in relation to the Equator and Tropics
Geographical Questions
- Can you track Ebo’s route from Niger into Sicily?
- Can you track a possible migrant’s route from Italy to the UK?
- Describe and explain some of the main reasons a migrant may need to leave their home country.
- How would you compare Agadez (Niger), with Tripoli (Libya) and European places you know?
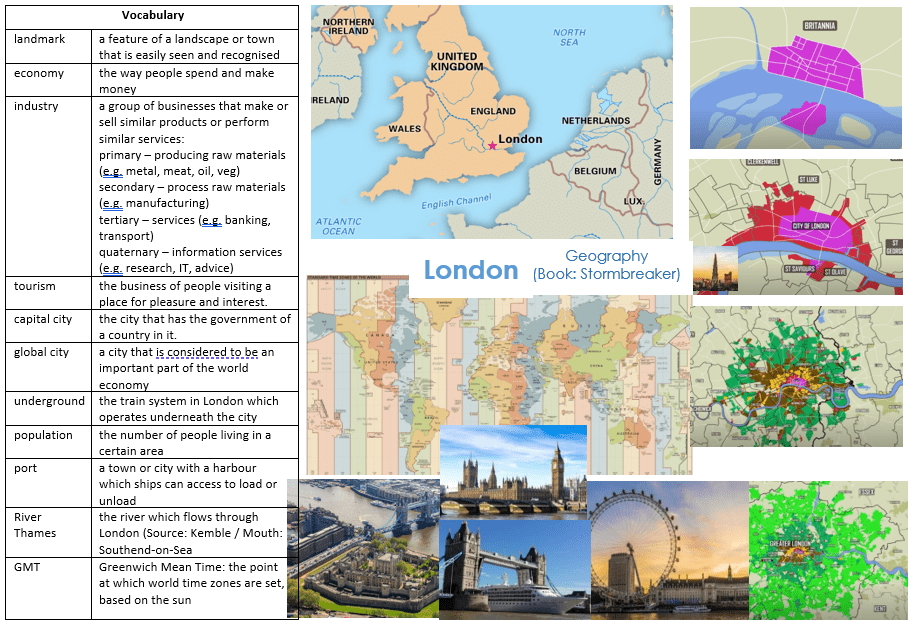
Year 5 London
As a geographer
- Use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and keys on Ordinance Survey Maps
KS1 (England [Leicester], Scotland [Inverness], China [Hong Kong])
Revise on world map:
- 7 Continents + 5 oceans
- UK: 4 countries and their capital cities
- Physical and human features
- Compass directions (N, S, E, W)
Geographical skills and fieldwork:
- Locate the UK on a world map / Locate London on a UK map
- Understand how London has grown since the formation of the Roman settlement to the current day city and how landuse around the city has evolved
- Understand why the city is a Global City: as a port and financial centre
- Identify the position of Greenwich Meridian and time zones
Geographical Questions
- Can you explain how and why London has changed over time?
- Can you explain why London is located on the Thames?
- Can you explain why London is a Global City?
- Which landmarks in London can you name?
- Can you explain why the world needs different time zones? How is London important to this?
- Which are the main industries in London? Can you explain why these are the main industries in London?
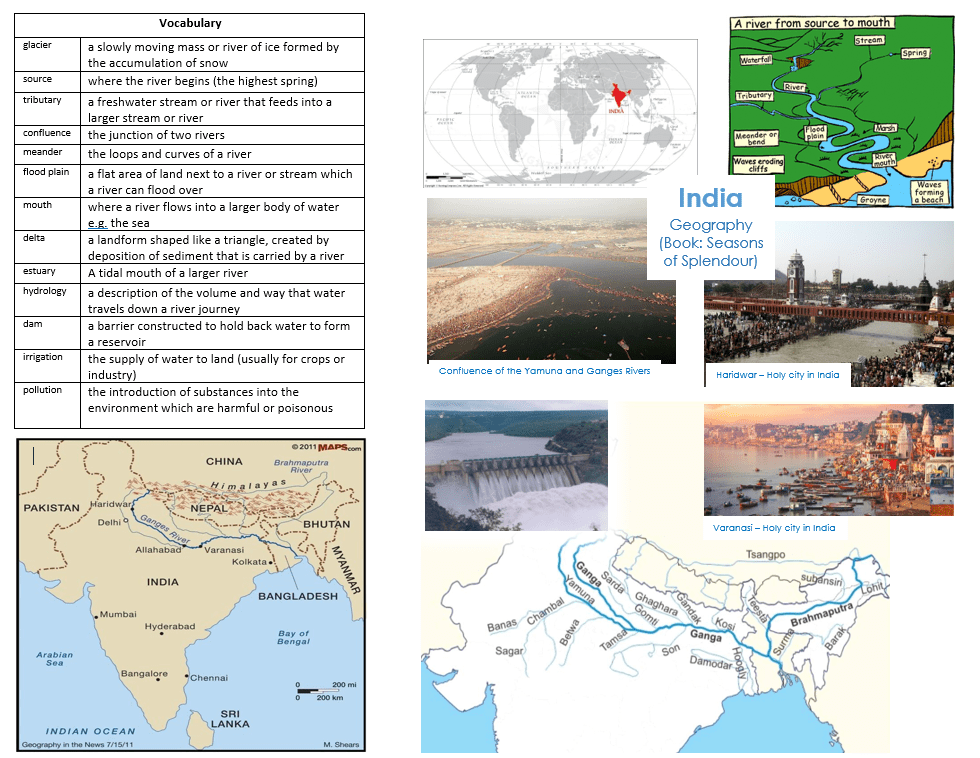
Year 6 Seasons of Spendour
As a geographer
- Create a model of the river cycle
- Measure, record and analyse rainfall
- Use aerial views and maps to consider the impact of pollution
- Use aerial views and maps to track The Ganges from source to mouth
KS1 (England [Leicester], Scotland [Inverness], China [Hong Kong])
Revise on world map:
- 7 Continents + 5 oceans
- UK: 4 countries and their capital cities
- Physical and human features
- Compass directions (N, S, E, W)
Geographical skills and fieldwork:
- Locate the continent Asia on a world map / Locate the countries India, Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan and Myanmar in Asia on a World map
- Understand the interaction between human processes (pollution (industry), irrigation & hydrology and religion) and the environment: the river journey
- Identify the position of India: latitude, longitude (Northern Hemisphere), and in relation to the Equator and Tropics.
- Identify the Ganges on a map of India, including its source, main tributaries, estuary, and mouth (Main Tributaries: Right: Yamuna and Son; Left: Gandak, Kosi and Brahmaputra
Geographical Questions
- Can you explain the human impacts on The Ganges River journey? (religion, pollution, C02 emissions, hydrology)
- Can you explain what the features of a river are?
- Can you explain how a river delta is formed?
- Can you explain why The Ganges River is significant to Hindus?
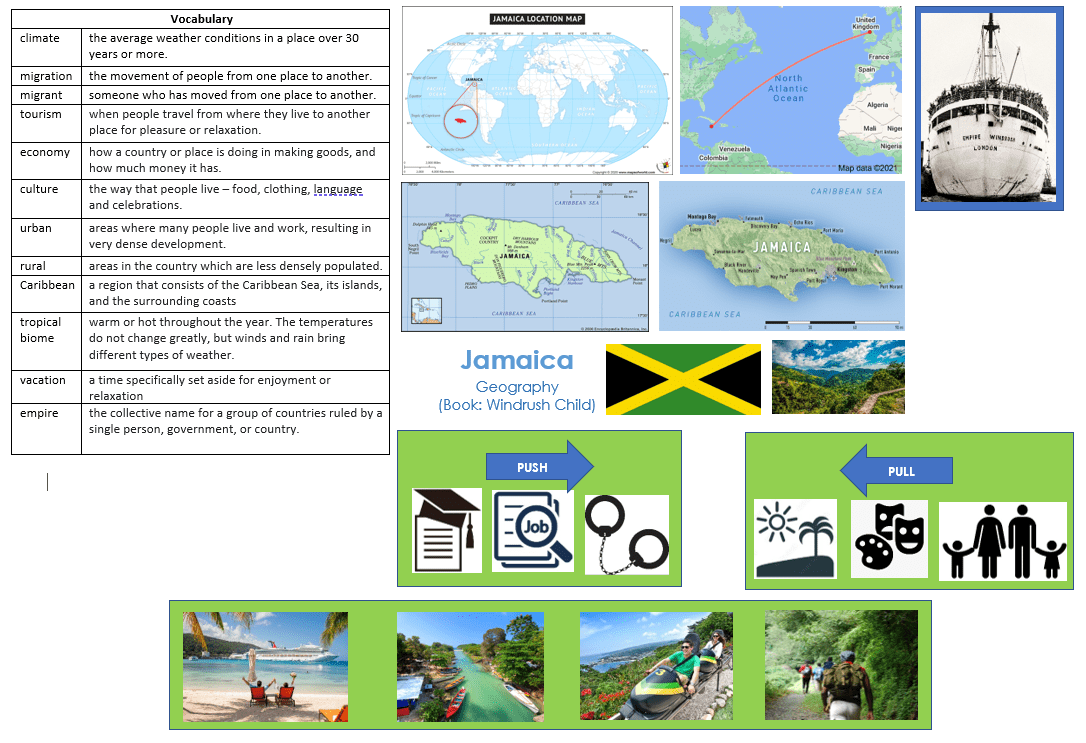
Year 6 Windrush Child
As a geographer
- Use digital maps to document the journey of migrants from Jamaica to London
- Use the eight compass points to refer to countries and features on a map.
KS1 (England [Leicester], Scotland [Inverness], China [Hong Kong])
Revise on world map:
- 7 Continents + 5 oceans
- UK: 4 countries and their capital cities
- Physical and human features
- Compass directions (N, S, E, W)
Geographical skills and fieldwork:
- Locate the continent North America on a world map / Locate the country Jamaica amongst the Caribbean Islands on a world map
- Locate Jamaica amongst the Greater Antilles Island Chain (Caribbean Islands)
- Locate the Caribbean Sea (part of the Atlantic Ocean)
- Locate Kingston, Maroon Town and The Blue Mountain National Park
- Compare coastal areas of Jamaica with central areas of the island
- Jamaica is a tropical biome; it is in the hurricane belt
- Tourism is the main industry in Jamaica
- Understand the interaction between human processes and the environment 1. Tourism: many tourists visit Jamaica 2. Migration: push and pull factors have influenced Jamaican people (especially in the post-war era e.g. The Windrush Generation)
- Identify the position of Jamaica: latitude, longitude (Northern Hemisphere), and in relation to the Tropic of Cancer
Geographical Questions
- Can you explain the importance of tourism to some countries?
- Can you explain why people would choose to migrate?
- How would you compare Leonard’s journey with Ebo’s journey? (Ebo from the book Illegal studies in Y5)
- How would you compare the Jamaican biome with Brazil, Hong Kong and South Africa?
Useful Websites
https://www.topmarks.co.uk/Search.aspx?Subject=12&AgeGroup=2
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/zcdqxnb
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/zbkw2hv
https://www.natgeokids.com/uk/teacher-category/geography/
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/zbkw2hv
https://www.ordnancesurvey.co.uk/mapzone/
GA Early Years and primary teaching resources (geography.org.uk)
Subject Leader/s
Mrs. R. Pattni













